Nvidia is continuing to release new products at quite a pace. Last month saw the arrival of RTX 2060 to generally favourable reviews, and today marks the official launch of GTX 1660 Ti. Long rumoured, this card is perhaps most notable for its distinct lack of any Tensor or RT cores – features which define the RTX series of graphics cards by giving them the ability to play ray traced games and use DLSS. With those features not supported here, we return to GTX nomenclature with the 1660 Ti.
Interestingly, Nvidia has not manufactured a Founders Edition for its new GTX 1660 Ti, instead it is relying on its board partners like ASUS, MSI and Gigabyte to produce a variety of cards. The MSI GTX 1660 Ti Gaming X 6G we are looking at today is definitely positioned as a high-end 1660 Ti, with a factory overclocked core and £50 price premium over the 1660 Ti's baseline MSRP of £259.
| GPU | RTX 2070 (FE) | GTX 1070 | RTX 2060 (FE) | GTX 1660 Ti | GTX 1060 |
| SMs | 36 | 15 | 30 | 24 | 10 |
| CUDA Cores | 2304 | 1920 | 1920 | 1536 | 1280 |
| Tensor Cores | 288 | N/A | 240 | N/A | N/A |
| Tensor FLOPS | 63 | N/A | 51.6 | N/A | N/A |
| RT Cores | 36 | N/A | 30 | N/A | N/A |
| Texture Units | 144 | 120 | 120 | 96 | 80 |
| ROPs | 64 | 64 | 48 | 48 | 48 |
| Rays Cast | 6 Giga Rays/sec | 0.65 Giga Rays/sec | 5 Giga Rays/sec | – | 0.44 Giga Rays/sec |
| RTX Performance | 45 Trillion RTX-OPS | 6.5 Trillion RTX-OPS | 37 Trillion RTX-OPS | – | N/A |
| GPU Boost Clock | 1710 MHz | 1683 MHz | 1680 MHz | 1770 MHz | 1708 MHz |
| Memory Data Rate | 14 Gbps | 8 Gbps | 14 Gbps | 12 Gbps | 8 Gbps |
| Total Video Memory | 8GB GDDR6 | 8GB GDDR5 | 6GB GDDR6 | 6GB GDDR6 | 6GB GDRR5 |
| Memory Interface | 256-bit | 256-bit | 192-bit | 192-bit | 192-bit |
| Memory Bandwidth | 448 GB/sec | 256 GB/sec | 336.1 GB/sec | 288.1 GB/sec | 192 GB/sec |
| TDP | 185W | 150W | 160W | 120W | 120W |
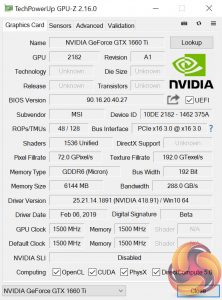
GPU-Z screenshot (left), TU116 GPU block diagram (right)
GTX 1660 Ti is still based on the same Turing architecture as all of the RTX 20-series cards we have reviewed over the past 6 months. We have detailed some key features of the Turing architecture in our initial reviews of the RTX 2080 and RTX 2080 Ti from September 2018.
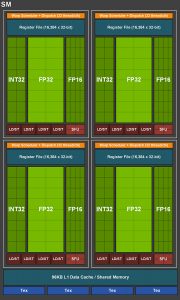
The primary difference here is that GTX 1660 Ti does not have any Tensor or RT cores. Rather than using the TU106 GPU (used for RTX 2060/2070) with disabled SMs and Tensor/RT cores, Nvidia created a new GPU for the GTX 1660 Ti, dubbed TU116 (as seen above).
TU102/104/106 SM (left), TU116 SM (right)
This is a consequence of Nvidia deciding that ‘adding dedicated cores to accelerate Ray Tracing and Al doesn't make sense unless you can first achieve a certain level of rendering performance', something it did not deem possible while also aiming the card at the ‘sub-$300 market.'
This has led to a slight revamp of the Turing SM design for TU116, primarily with the addition of the dedicated FP16 cores. Nvidia claims modern games are ‘increasingly using FP16 to create effects that don't require a high level of precision', and where this is handled by the Tensor cores on the RTX cards, there are now dedicated FP16 cores within TU116 which can process at double the rate of FP32 operations.
In total, TU116 sports 24 SMs, each with 64 CUDA cores – giving a total of 1536. It is also worth making clear, if not already, that GTX 1660 Ti still supports other Turing technologies we have already detailed – including variable rate shading and concurrent execution of FP/INT instructions, for example. The major difference between 1660 Ti and the RTX cards is, as mentioned, no support for ray traced games or DLSS.
Other changes to note with the GTX 1660 Ti include the 6GB GDDR6 memory. Where we have previously seen GDDR6 operating at 14 Gbps, with the 1660 Ti this is slightly slower, with a 12 Gbps data rate. Also on the topic of speeds, reference GTX 1660 Ti has a boost clock of 1770 MHz, though this factory overclocked MSI Gaming X model has increased that to 1875 MHz.
Lastly, reference TDP is rated at 120W, the same as GTX 1060. Our MSI Gaming X ups this to 130W thanks to its increased out of the box clock speed.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards