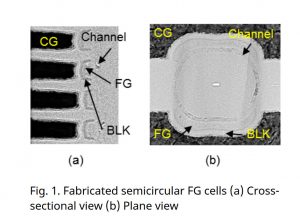
Kioxia recently announced it has developed a new flash memory cell structure. Twin BiCS FLASH is the world’s first three-dimensional semicircular split-gate flash memory cell structure using specially designed semi-circular Floating Gate cells.
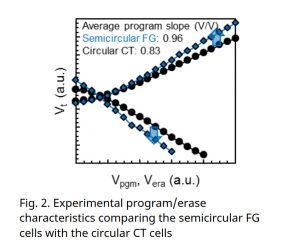
The new memory cell structure from Kioxia achieves greater program slope and larger program/erase windows with a much smaller cell size, compared to conventional circular designed Charge trap cells. All these attributes of the semi-circular cell design make it a promising candidate to surpass four bits per cell (QLC) and provide higher memory density with fewer stack layers.
The new technology was announced at the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting that was held in San Francisco earlier this month. In recent years, 3D flash memory technology has achieved a higher bit density with low cost per bit by increasing the number of stacked cell layers. Since the number of cell layers exceeded 100, managing trade-offs between etch profile control, size uniformity and productivity has become more challenging.
To overcome these problems, Kioxia developed the new semi-circular cell design that split the gate electrode in the conventional circular cell which reduces the cell size, therefor enables higher-density memory with a lower number of cell layers. Kioxia claims the semi-circular Floating Gate (FG) cells have superior program/ease characteristics and are expected to attain tight QLC Vt distributions and small cell size.
Kioxia believes that semi-circular FG cells are a viable option to pursue higher bit density and moving forward, the company’s R&D efforts will be aimed at continuing Twin BiCS FLASH development and finding its practical applications.
Discuss on our Facebook page HERE.
KitGuru says: What do you guys think to this new Twin BiCS FLASH with semicircular cell design? Will it be the future for memory cell structure design?
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards