The ADATA XPG SX950 240GB drive comes in a compact box, the front of which has an image of the drive together with the model number, capacity, the fact it uses 3D NAND and sequential read/write performance figures together with neat flame coloured swoosh type graphic.
The rear of the box has some multilingual marketing details, the read/write performance figures again and a couple of QR codes that access the XPG website.
The drive is bundled with a spacer to use the drive in notebooks with 9mm drive bays, a 3.5in to 2.5in drive bay converter and a warranty booklet.


The drive is built on a standard 2.5in, 7mm format with a decent quality metal case with the same swoosh graphic that is on the box front but in a vertical position.


Inside the enclosure sits a compact half size PCB with the Silicon Motion SM2258 controller, two packages of 3D MLC NAND which although are labelled as ADATA are produced by Micron and the 128MB Nanya DDR3L cache IC. The rear of the board houses two more NAND packages.
The Silicon Motion SM2258 is a 4-channel controller using a 32-bit RISC processor supporting 1z nm TLC and 3D MLC/TLC NAND. It supports LDPC ECC technology and has pseudo-SLC caching support.
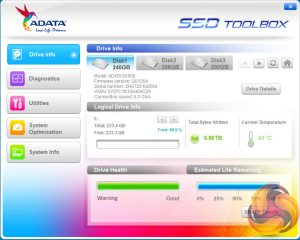


ADATA's management utility for their SSD's is called the SSD Toolbox and it certainly catches the eye as it's about the most colourful looking utility out there. The drive info page displays information about how much capacity is being used and the TBW number.
It also shows the drives temperature, health and how much estimated life the drive has left. There's also a button that links to the S.M.A.R.T. table.
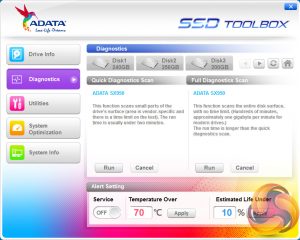
The diagnostics section allows you to perform either quick or full diagnostic scans of the drive and to set the alarms for when the drive gets too hot or gets close to its end of life.
The utilities page is home to the secure erase function and it's also the page where you can update the firmware and the toolbox software and export any logs you have created.
The system optimisation page allows for some OS settings to be changed using two settings Basic or Advanced. Basic options include changing Superfetch, Prefetch, and Automatic Defrag settings.
Advanced changes settings for, Hibernation, NTFS Memory Usage, Large System Cache, Superfetch, Prefetch, and System File in Memory.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards





