Protection Features
Our protection features evaluation methodology is described in detail here.
|
Protection Features |
|
|
OCP |
12V: 50.6A (134.93%), 12.039V |
|
OPP |
622.9W (138.42%) |
|
OTP |
✓ (140°C @ Secondary side) |
|
SCP |
12V: ✓ |
|
PWR_OK |
Accurate (but lower than 16ms) |
|
NLO |
✓ |
|
SIP |
Surge: MOV |
With the only exception being the 3.3V rail, all the rest of the voltages have ideally configured over current protection triggering points. Moreover, the over temperature protection works well and gets activated once the temperature in the secondary side reaches 140°C.
The over power protection is set a little higher than the ideal 130% setting, however this is a low capacity supply so Corsair probably wanted to avoid any problems with power spikes, which can be generated by high-end GPUs.
There is short circuit protection on all rails and the power ok signal is accurate, but it is lower than 16ms which is the minimum period allowed by the ATX spec.
Finally, there is a Metal Oxide Varistor which protects not only the power supply but the whole system from power surges coming from the mains grid, while a NTC thermistor and bypass relay combo suppress the high inrush currents, during the PSU's start-up phase.
DC Power Sequencing
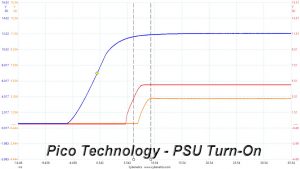
According to Intel’s most recent Power Supply Design Guide (revision 1.4) the +12V and 5V voltages must be equal or greater than the 3.3V rail’s output at all times, during the power-up and normal operation. For our first measurement, we turn the unit off and switch it back on without any load in any of the rails.
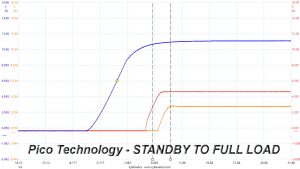
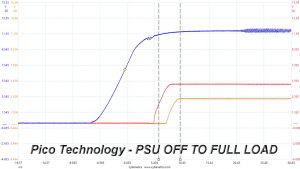
In the second test, we set the PSU to standby mode, dial full load and start it afterwards. In the last test, while the power supply is completely switched off (we cut off the power or switch the supply off through its power switch), we dial full load before restoring power.
The 3.3V rail is always lower than the 5V and 12V rails, so the power supply passes with success the required, by Intel's ATX spec, DC power sequencing tests.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards