Manual CPU Overclocking:
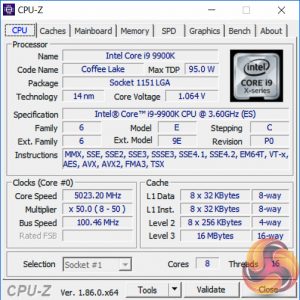
To test the MSI MEG Z390 ACE motherboard’s CPU overclocking potential, we set the CPU core voltage no higher than 1.3V and push for the highest stable clock speed. We maintain the DRAM frequency at 3200MHz to take memory stability out of the overclocking equation.
Our particular CPU is not stable at 5.1GHz even with 1.45v. The final stable overclock for almost all Z390 motherboards we may test should be 5GHz, unless there is something particularly wrong with the VRM that limits the voltage or power it can supply. In the case of the MSI MEG Z390 ACE it achieved 5GHz at 1.3 volts with no significant issues.
Motherboard Sensors
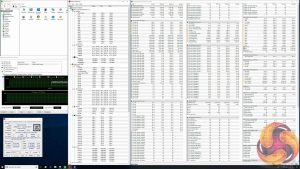
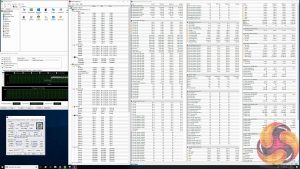
MSI has specific sensors for monitoring the temperature and power delivery of the VRM solution. During testing we found at stock (1.22v vCore) and overclocked (1.3v vCore) the temperatures held around 70 degrees Celsius, which is very healthy indeed.
If the VRM sensors are to believed then the efficiency of MSI's VRM solution is about 82%, which is also a respectable number.
Overclocked Performance
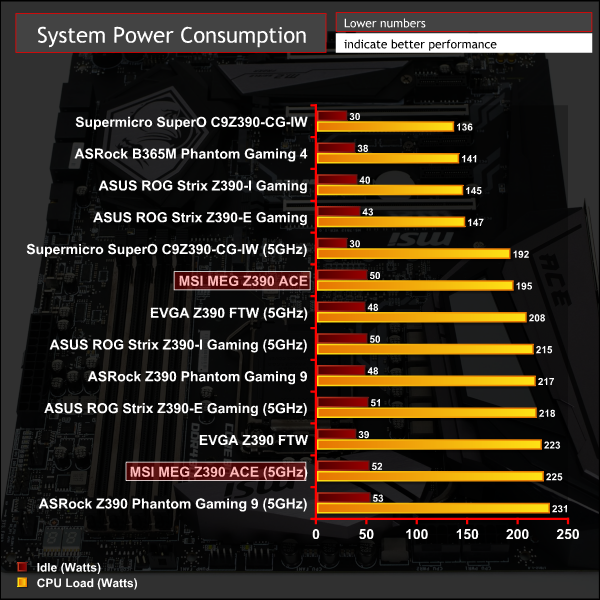
System Power Consumption
We leave the system to idle on the Windows 10 desktop for 10 minutes before taking a reading. For CPU load results we run AIDA64 CPU, FPU, Cache and Memory stress tests and take a reading after 10 minutes. The power consumption of our entire test system (at the wall) is shown in the chart.
12-volt EPS Power Consumption
During the 10-minute stress test as specified above, we record the direct CPU power consumption drawn through the EPS 8-pin socket using modified EPS 8-pin cables that have a Tinkerforge Voltage/Current 1.0 bricklet intercepting and monitoring the power flow from the power supply. That bricklet then reports its data to a Tinkerforge Master Brick. All the data collected by the Tinkerforge Master Brick is passed into an external laptop over a USB connection and analysed in the Cybenetics Powenetics Project software.
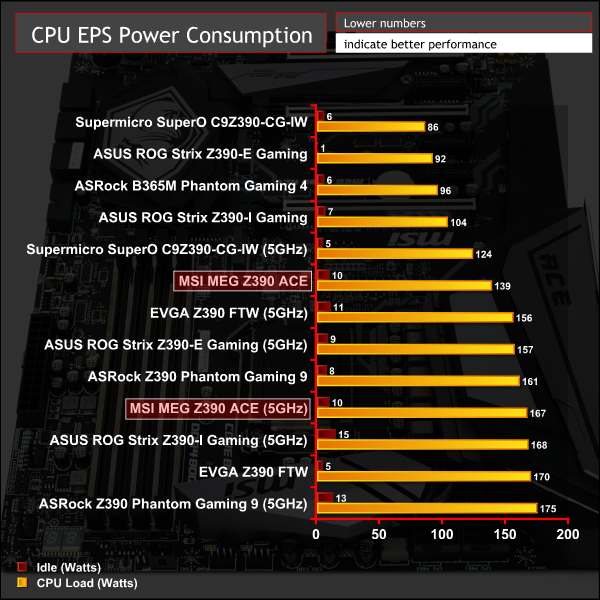
System power consumption was consistent and as-expected for the frequencies and voltages applied.
“Stock” power consumption is higher than many rival motherboards, but that is due to MSI disregarding Intel's Turbo specifications rather than inefficiency on MSI's part.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards