We measured the power consumption with the system resting at the Windows 7 desktop, representing idle values.
The power consumption of our entire test system (at the wall) is measured while loading only the CPU using Prime95′s in-place large FFTs setting. The rest of the system’s components were operating in their idle states, hence the increased power consumption values (in comparison to the idle figures) are largely related to the load on the CPU and motherboard power delivery components.
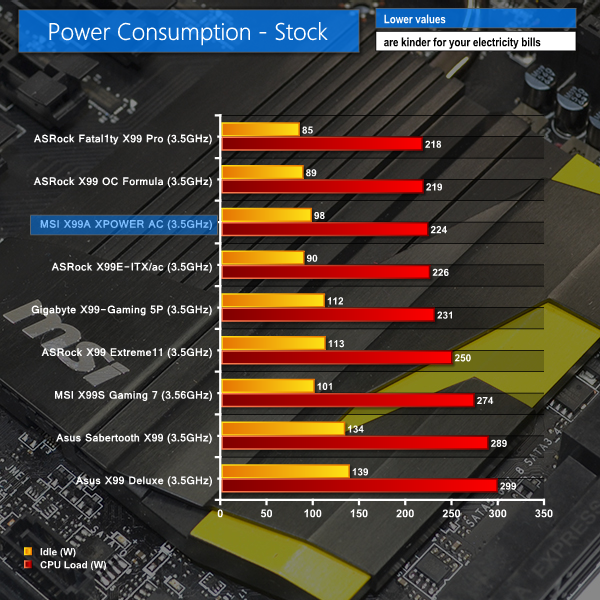
Stock-clocked load and idle power consumption numbers are positive for the X99A XPOWER AC. This result point towards a well-managed, efficient power delivery system. Idle values dip below 100W thanks to the controller's ability to rapidly drop system voltages under low loads.
Overclocking the MSI X99A XPOWER AC results in mediocre power consumption levels while loaded. The constant voltage level results in high idle power draw though. Clearly the override voltage section in MSI's UEFI is actually overriding the voltage level all of the time.
This may be considered a positive when pushing for higher overclocks where system instability can come at any point or load level – high idling voltage increases the chance of maintain system stability.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards




Your first choice kitguru