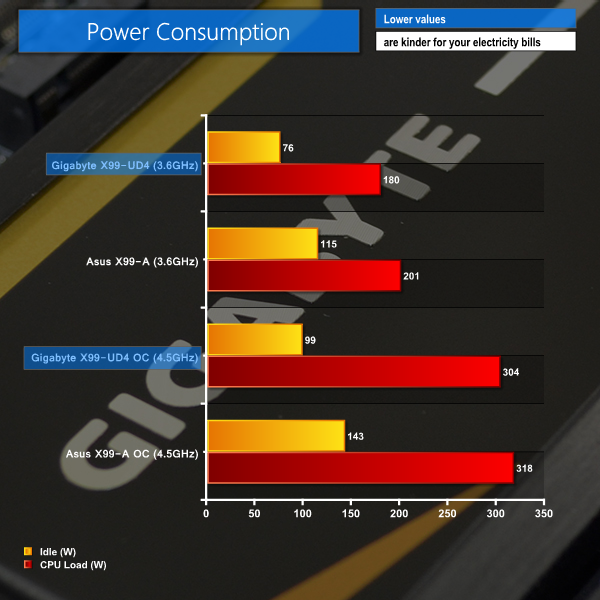
We measured the power consumption with the system resting at the Windows 7 desktop, representing idle values.
The power consumption of our entire test system (at the wall) is measured while loading only the CPU using Prime95′s in-place large FFTs setting. The rest of the system’s components were operating in their idle states, hence the increased power consumption values (in comparison to the idle figures) are largely related to the load on the CPU and motherboard power delivery components.
Gigabyte's digitally-controlled voltage system dynamically adjusts the CPU VCore level to strike a balance between power consumption and clock speed under low load conditions. This translates into excellent power usage numbers when idle, shaving around 40W off the levels shown by Asus' X99-A.
Even at full load, Gigabyte's X99-UD4 continues to show its efficiency by consuming 14-21W less power than Asus' X99-A. The high-spec Cooper Bussmann chokes and International Rectifiers 3553M MOSFETs seem to have been a smart design choice for power efficiency.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards