Manual CPU Overclocking:
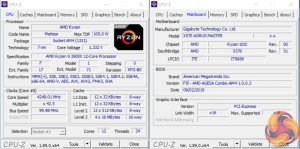
To test the Gigabyte X570 Aorus Master motherboard’s CPU overclocking potential, we set the CPU Core Voltage to 1.35V and applied the High LLC setting.
We were able to hit a stable frequency of 4250MHz using 1.35V. The Gigabyte X570 Aorus Master motherboard forced us to apply the High load-line calibration setting in order to keep close to 1.35V under load.
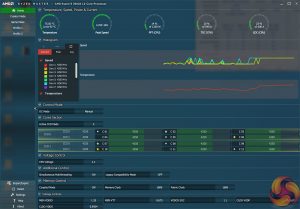
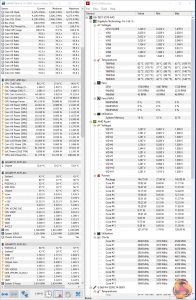
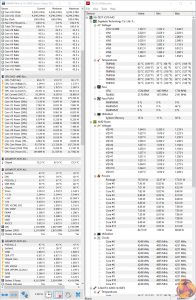
Motherboard Sensors
Overclocked Performance
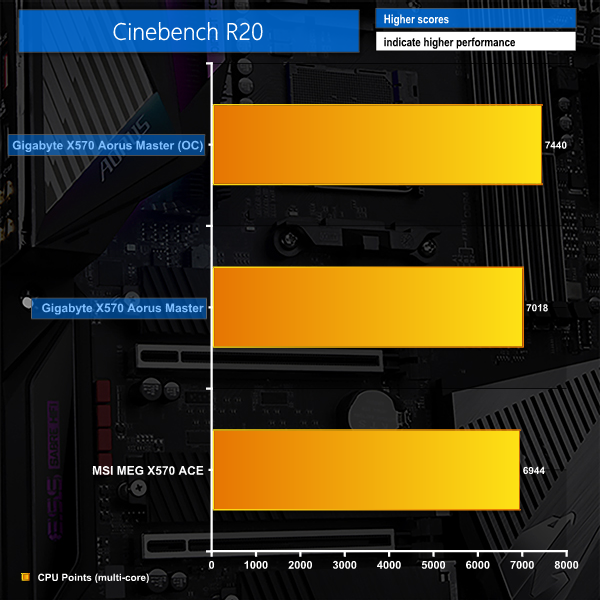
Increasing the Ryzen 9 3900X CPU’s clock speed to 4250MHz delivered a solid performance improvement of 422 points or 6% in Cinebench R20. Of course, the reduced peak clock speed for lightly-thread workloads will be a limitation so this overclock setting is better suited for users with heavy multi-threaded tasks.
System Power Consumption
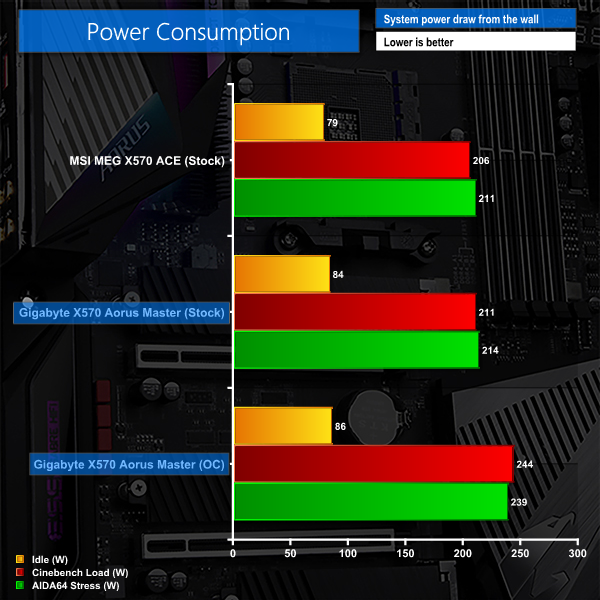
We leave the system to idle on the Windows 10 desktop for 10 minutes before taking a reading. For CPU load results we run AIDA64 CPU, FPU, and Cache stress tests and take a reading. The power consumption of our entire test system (at the wall) is shown in the chart.
Unsurprisingly, given its slightly higher performance thanks to higher boost clock speeds, Gigabyte’s X570 Aorus Master draws slightly more power than the MSI competitor. With that said, there’s only a handful of Watts in the difference between these two motherboards.
Overclocking the CPU forces a power consumption increase in the order of 30 Watts. It is good to see that the idle power draw barely changed with the system overclock.
System Temperatures
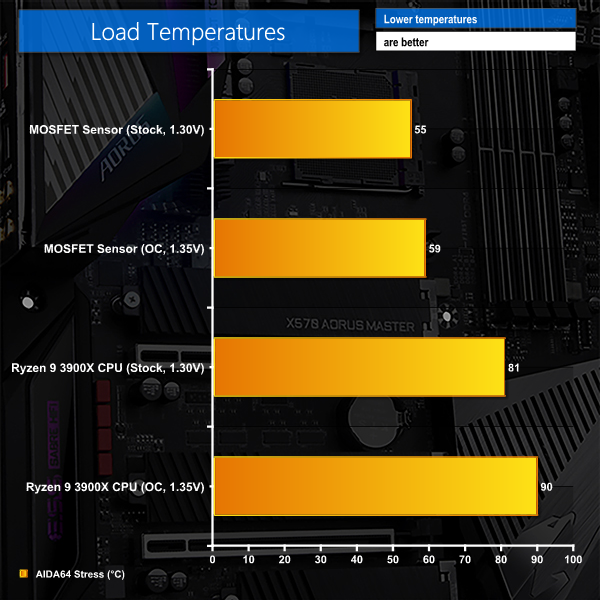
We run the AIDA64 CPU stress test for 1 hour while recording the system data using HWInfo. This data is then analysed to show the CPU temperatures and also the VRM MOSFET temperatures, when the sensor data is available.
Gigabyte's VRM heatsink does a superb job at managing the heat thrown its way. Even with a 1.35V overclock on the Ryzen 9 3900X (and validated with a multimeter), the MOSFET sensor stayed at a maximum of 60°C after 1 hour of heavy AIDA64 stress testing. And that's just with the incidental airflow from a Corsair H100X AIO in an open test bench configuration, not a chassis or air cooler with better airflow scenarios.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards