Performance and Testing
We explain our testing methodology in our video at some length. In essence we built two test systems using very similar hardware. The first system is built around the Ryzen 7 8700G while the second uses an Intel Core i5-14600K that is limited to the same 65W as the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G. Here is a breakdown of the two test systems.
AMD System
- CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 8700G
- CPU Cooler: AMD Wraith
- Motherboard: MSI B650 Gaming Plus WiFi
- RAM: 32GB G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo RGB DDR5-6400 C34
- Graphics: AMD Radeon 780M and Gigabyte Radeon RX 6500 XT Eagle 4GB
- SSD: 1TB Sabrent Rocket 4 Plus
- Power Supply: Seasonic Focus GX-1000 Gold
Intel System:
- CPU: Intel Core i5-14600K
- CPU Cooler: Intel RM1
- Motherboard: Gigabyte Z790 Aorus Elite AX
- RAM: 32GB G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo RGB DDR5-6400 C34
- Graphics: Intel UHD Graphics 770 and Gigabyte Radeon RX 6500 XT Eagle 4GB
- SSD: 1TB Sabrent Rocket 4 Plus
- Power Supply: Seasonic Focus GX-1000 Gold
CPU Performance and Testing
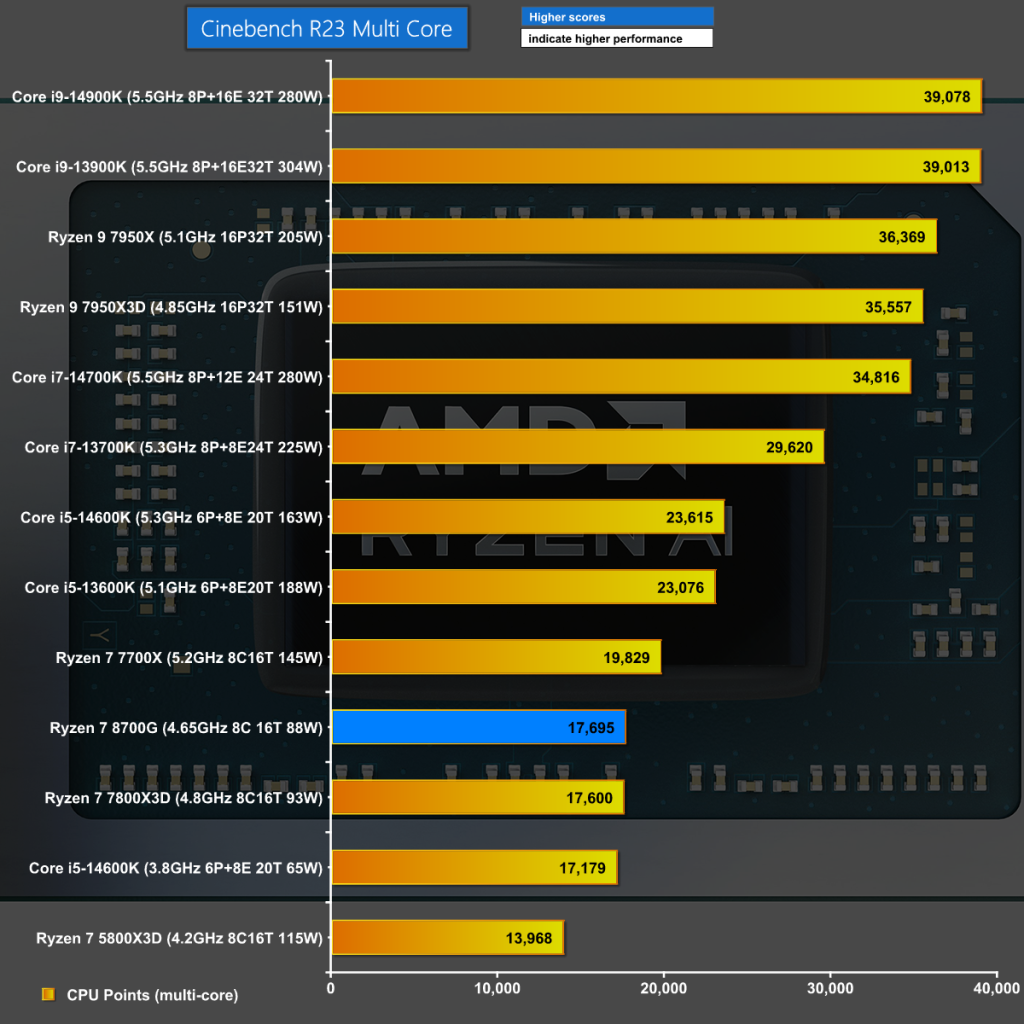
Cinebench R23 Multi Core
In Cinebench R23 Multi Core the Ryzen 7 8700G runs at 4.65GHz on all cores which is significantly slower than the eight-core Ryzen 7 7700X and consequently it delivers lower performance. As we will see in the next chart this is a simple matter of clock speed versus power draw.
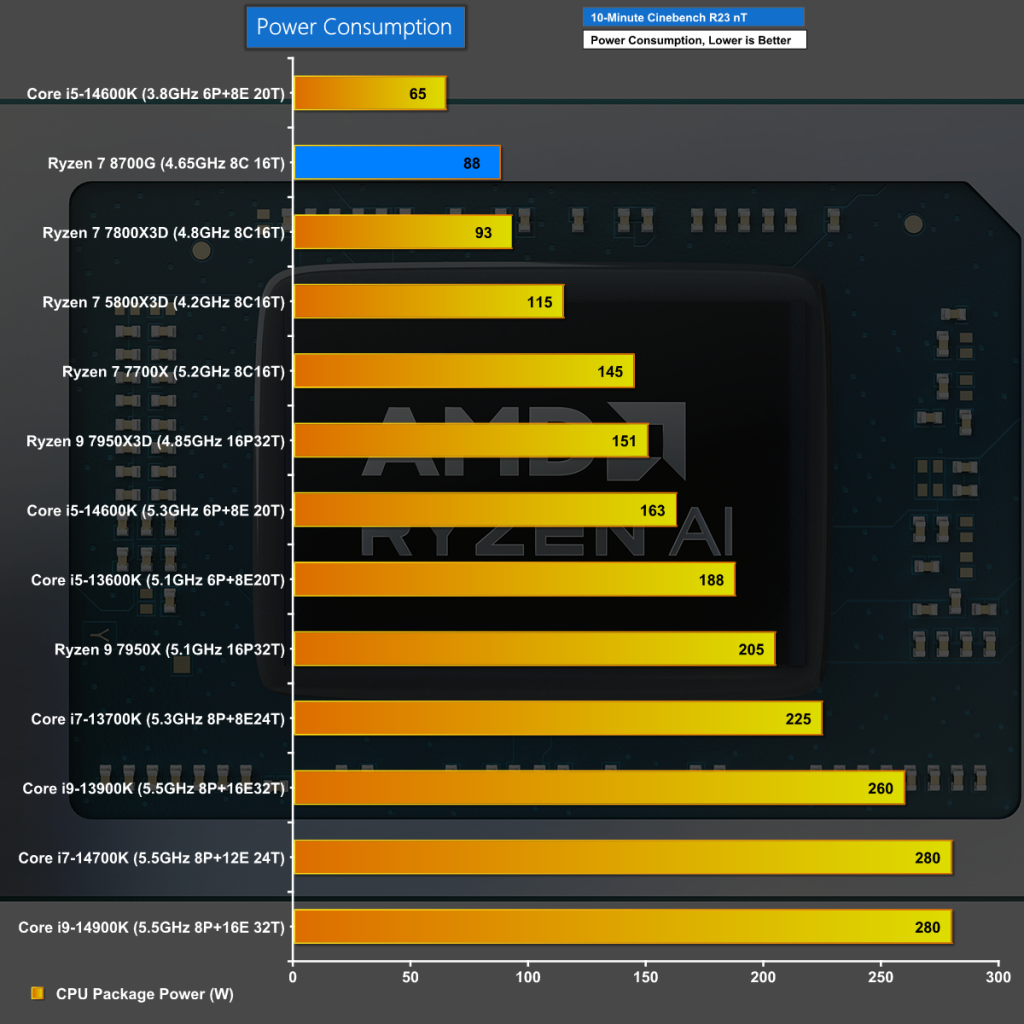
Clock Speeds and Power Draw
We can see the Ryzen 7 8700G draws 88W under load which is far less than we typically see with a desktop Ryzen 7 CPU. This demonstrates the laptop origin of the hardware where 88W is a relatively high number.
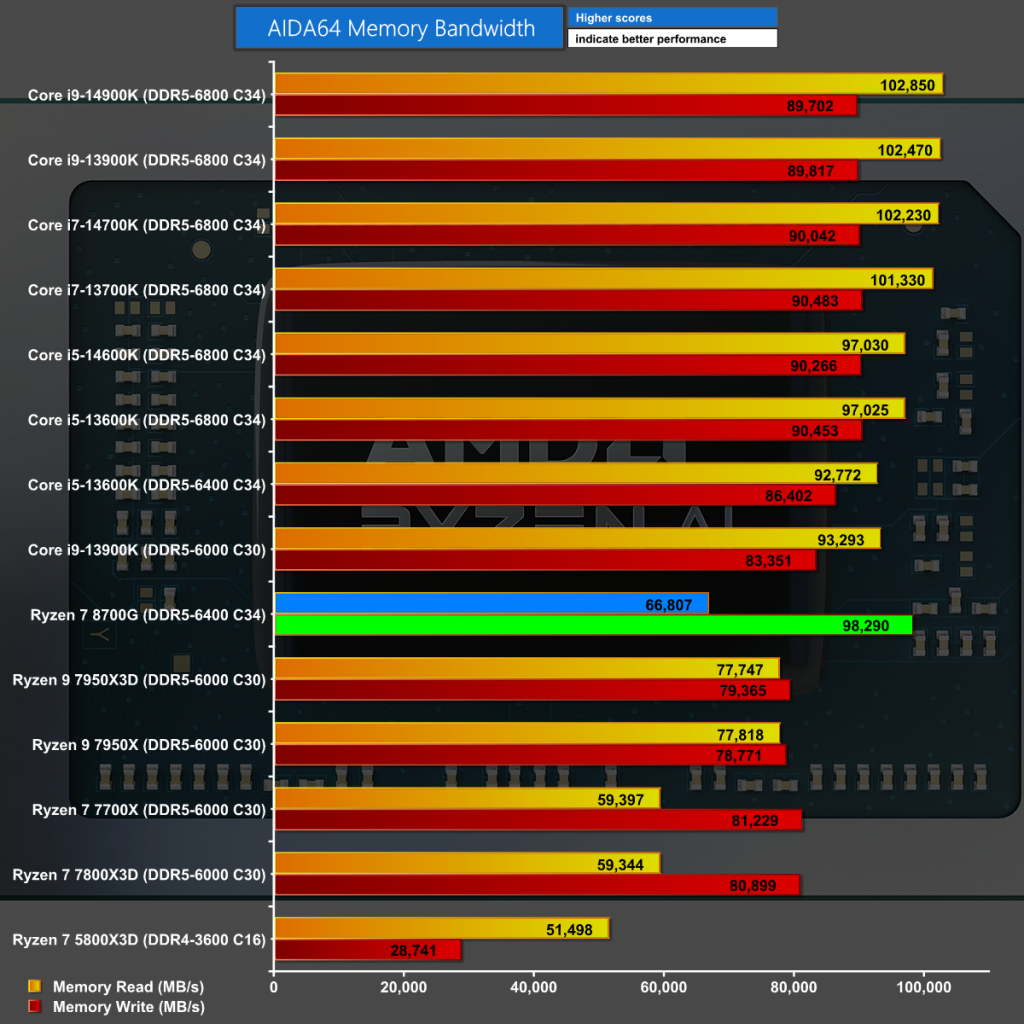
AIDA64 Memory Bandwidth
In AIDA64 Memory Bandwidth we see the impact of faster DDR5 memory on the benchmark, but we also have to consider the way that AMD works with memory compared to Intel. The result is that the Ryzen 7 8700G writes to DDR5-6400 impressively fast and reads at a decent speed.
 KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards
KitGuru KitGuru.net – Tech News | Hardware News | Hardware Reviews | IOS | Mobile | Gaming | Graphics Cards